ServiceNow Express Knowledge Management
ServiceNow Express Demo
Everything as a Service
HR Service Management
Outsmart Service Outages
Deliver Stellar Service Experience
Work Smarter, Not Harder: Employee Onboarding
Solving a Security Crisis
Performance Analytics: Dashboards
Performance Analytics: Data Collection
ServiceNow Developer Site
Insert Images into Forms and KB Articles
Asset Management
Asset management integrates the physical, technological, contractual, and financial aspects of information technology assets.
An IT asset is any company-owned information, system or hardware that is used in the course of business activities. Assets can be many different types of items in a company. ServiceNow has over 126 categories of assets available in their base system.
Benefits of Asset Management
- Control purchased inventory and usage while reducing costs
- Manage the asset life cycle from planning to disposal of strategic assets
- Achieve compliance with relevant process, standards, and regulations
- Improve the end-user experience with faster procurement and deployment of assets
Difference between Asset Management and Configuration Management (CMDB)
One of the confusing parts of ServiceNow is why there is a CMDB and Asset Management. The reason why can be summed up in this statement:
Asset management and configuration management (CMDB) are related, but have different goals. Asset management focuses on the financial tracking of company property. Configuration management focuses on building and maintaining elements that create an available network of services.
Once you have that CMDB framework, use Asset Management to make it even more valuable. Put a cost to Configuration Items, make sure servers and laptops are deployed and retained properly. Build the CMDB using discovery, but pay with it using Asset Management.
What is the difference between an Asset and Configuration Item (CI)?
Asset
- Track the financial aspects of the item purchase, cost, and depreciation of the item.
- Contracts, Maintenance, Warranty, and Licensing tied to the item.
- Inventory tracking is expected to meet obligations.
- Document the status of the item, build, and decommission status.
Configuration Item
- Record the technical attributes of the item
- Relationships to other Configuration Items
- Associated with an Incident, Problem, Change, or any task.
Read more about how Assets and Configuration Items are synchronized:
GETTING STARTED
Identify Assets

Another year of inventory soon!
I grew up in my parents hardware store in central Minnesota. As soon as I was able to count, I was participating the yearly manual counting of every item in the store.
For some reason, I enjoyed the process of counting and learning what every item did in the store. I had my first wife try it one year...she did not have the same enthusiasm.
The good news is that for IT departments, there are modern innovations to really help automate this process:
- ServiceNow Discovery
- Service Mapping
- Help the Help Desk
- Integrations
- Handheld Scanning and RFID tags
After you get the data imported, you can start to analyze it. Asset Management has a starter homepage available for usage. It is located in the Left Nav Bar under Asset > Overview. Roles that can view the Asset Overview page are admin, asset, and sam.

Asset Overview
Categories, Models, and Classes
If you are using ServiceNow Discovery, a lot of Asset Management is created for you. However it often requires some additional configuration. Models in particular sometimes require some normalization and refinement so you can get proper reports.
- Models. Models are specific versions or various configurations of an asset, such as a MacBook Pro 17".
- Model Categories. Categories of asset models can be items such as computers, servers, printers, and software. Model categories associate CI classes with asset classes. The model category configuration determines if ServiceNow should create an asset from a CI and if so, what class of asset. This is straightforward how the Model Categories work. If you a certain CI, for example, Computer [cmdb_ci_computer], to create and update an related asset, it must have a model category.
- Asset Classes. The default asset classes are Hardware, Software License, and Consumable. These general classes can be used to manage most assets. Creating a new asset class requires defining a new table and creating a corresponding application and module, then adding the new asset class to new or existing model categories. Read about it here
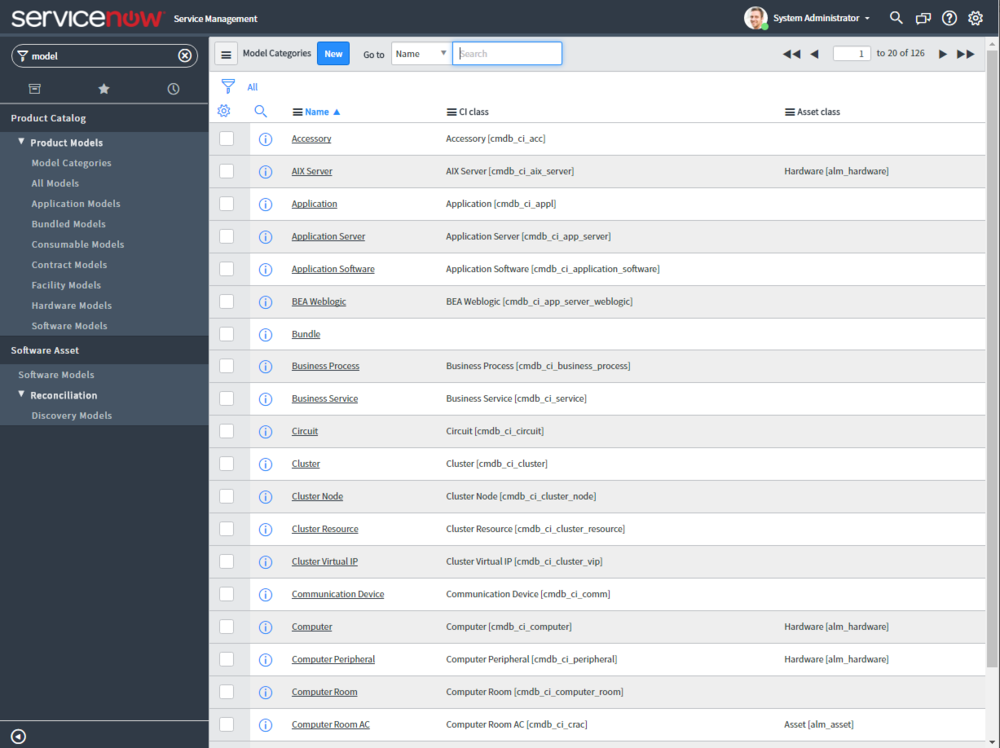
Model Categories

Models
Table Structure
Asset Management uses a variety of tables and it is tough to keep up with all the tables involved. The most important table to remember is the main Asset [alm_asset] table. However reading about the tables helps show how Asset Management works:
- Asset [alm_asset]: Stores general, financial, and contractual information about assets.
- Asset Entitlement [alm_entitlement_asset]: Enables ServiceNow to categorize the Asset Entitlement table and enforce how entitlements behave.
- Consumable [alm_consumable]: Stores data about consumable assets (previously known as parts).
- Default Stockroom [alm_user_stockroom]: Stores the relationship between a user and their default stockroom.
- Fixed Assets [alm_fixed_assets]: Stores fixed assets, which are containers that can hold multiple assets.
- Fixed asset to asset [m2m_fixed_asset_to_asset]: Stores associations between fixed assets and assets.
- Hardware [alm_hardware]: Stores general, financial, and contractual information about hardware assets.
- License Entitlement [alm_entitlement]: Stores entitlements that permit users or machines to use a software license.
- Software License [alm_license]: Stores general, financial, and contractual information about software license assets.
- Stock Rule [alm_stock_rule]: Transfers stock or sends an email message to the asset manager when a specified asset drops below a set threshold.
- Stockroom [alm_stockroom]: Stores information about stockrooms.
- Stockroom Model [alm_m2m_stockroom_model]: Tracks all models that have ever been stocked in a stockroom. This table is automatically populated.
- Stockroom Type [alm_stockroom_type]: Stores general information about stockroom types.
- Transfer Order [alm_transfer_order]: Contains data about transfer orders, including the state and stockrooms.
- Transfer Order Line [alm_transfer_order_line]: Contains data about individual assets being shipped with a transfer order.
- User Entitlement [alm_entitlement_user]: Enables ServiceNow to categorize the User Entitlement table and enforce how entitlements behave.
ASSET MANAGEMENT PROCESS
After you get the initial data imported and updated the best you can, then you can begin using asset management in your daily work!

Asset Management Process
Acquisition
If you are hooked up to Discovery or another integration to import assets, this setup is much easier for you.
You can create assets manually if you don't have an automatic asset creation or have assets that are not automatically discovered.
You may also use optional Purchase Order and Receive Assets functionality to order assets from an vendor and keep track of that within ServiceNow.
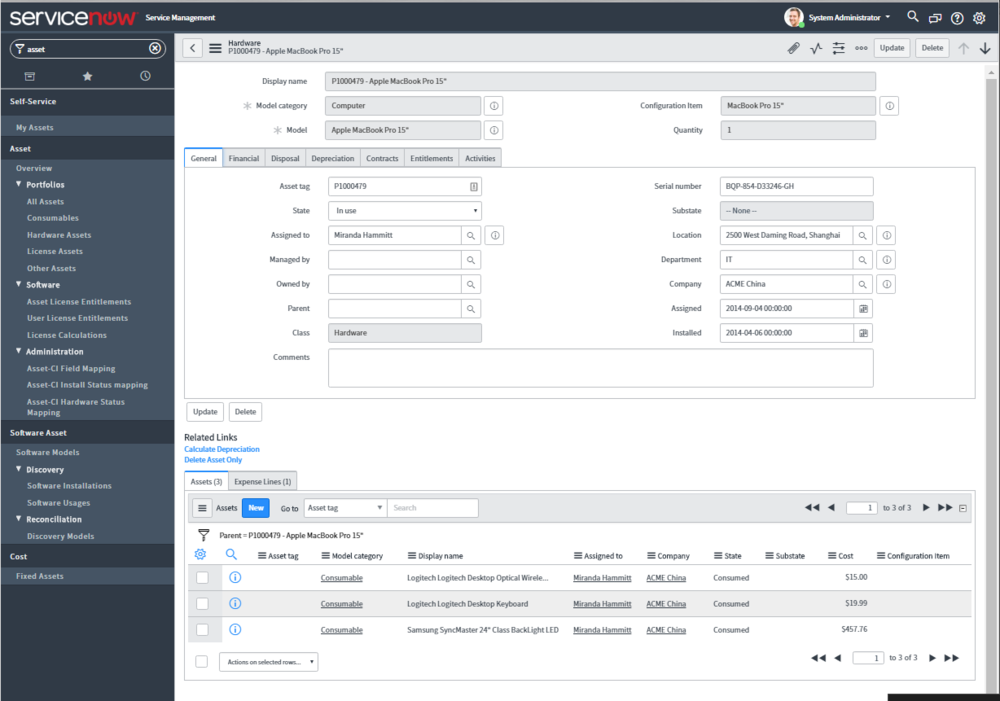
Asset Detail
- Financial. Capture financial information such as invoicing and cost center chargeback.
- Disposal. Track disposal reasons, resale price, and retirement date.
- Depreciation. File the depreciation information on the asset.
- Contract. Leases, Warranty, Support Group and contract info
- Entitlements. Software licenses and other hardware entitlements tied to the asset.
- Other Asset Relationships. See consumables like keyboards, monitors, and peripherals tied to the asset.
Manage assets by counting software licenses, viewing assets that are in stock, setting asset states and substates, and analyzing unallocated software.
Deployment
Acquistiion and Deployment blend together at times. However there is a point when you adjust the asset state and mark it "in use".
Along with simple state field adjustments, the process for deployment may be dramatically different (and complex) for companies. Some may use a workflow or orchestration to update other systems, generate tasks for people to complete tasks in the deployment process. It can be as complicated as you want it.
Utilization
Once you have the asset ready to be used, you can use a variety of method to track utilization.
- Transfer Orders. Transfer orders move assets between company stockrooms.
- Stockrooms. Stockrooms are places to which assets are assigned.
- Stock Rules. Stock rules are defined criteria stating that when inventory of a particular asset in a particular stockroom reaches a specified threshold, a certain number should either be transferred from another stockroom or ordered from a vendor.
Maintenance
There are many different tasks to keep your asset management system with reliable data and great functionality. Here are couple tips:
- Asset Sync. Assets and Configuration items will likely need adjustment in the sync process. Read about that here
- Focus on Quality, not Quantity. It is often tempting to push everything you have into asset management. However this doesn't necessarily insure maximum value. It will make things difficult to find and the user experience will suffer. Also it is advised to only create an asset when you are using it for financials. I say to concentrate your efforts on making each asset great, not a great number of assets.
- Watch Update Frequency and Sequence. If you have multiple discovery sources and integrations that feed into Asset Management, it is good to watch how they update field data the order. In some cases, discovery sources may compete with each other, flipping field values back and forth with each update.
- Avoid Duplicates. One of the worst things that can happen in ServiceNow is duplicate records. They are difficult to remove and cause havoc with reporting and ease of use. Read how you can look for it here: Duplicate Record Scripts
Retirement
The opposite of the deployment phase, retirement may involve some state field changes and different processes to retire and decommission the asset. Like deployment, this can also be as complicated as you would like.
MORE INFORMATION
Here is an additional video on Asset Management
ServiceNow Product Catalog
Here are the collected works of this site organized by ServiceNow product lines.
Service management
IT Service Management
IT Operations Management
IT Business MANAGEMENT
ServiceNow Express
INTEGRATIONS
UPGRADES
Procurement
Procurement managers can use the ServiceNow Procurement application to create purchase orders and to obtain items for fulfilling service catalog requests.
Procurement offers the ability to perform the following functions.
- Track service catalog requests
- Create and manage purchase orders
- Create and manage transfer orders
- Receive assets
Plugin
The Procurement application requires the "Procurement" plugin to be activated before use.
Process
1. Order Submit. User places an order from the service catalog

Order Submit
2. Over $1000. In the Service Catalog Request workflow, items ordered from the service catalog that cost over one thousand dollars require approval. If under $1000, they are automatically approved.

Service Catalog Request

Service Catalog Request Workflow
3. Approval. If the request is approved it moves to the next step.
4. Sourceable? There is a business rule, Can request be sourced, that checks the items submitted with the request to determine if the request can be sourced. It checks if the item has a model specified.
5. Catalog Task Generation. In the Source Request workflow, a catalog task is created so that a procurement manager can source the item by creating a transfer order or purchase order.

Source Request Workflow
There is a "Source Request" button on the catalog task that the Procurement person can click

Source Request button on Catalog Task
7. Source Request. If the source request is clicked on the catalog task. A source screen is shown

Source Request Methods

Source Screen
- Purchase Order - You can create a purchase order directly from a request. This enables procurement managers to obtain items and fulfill requests from the Service Catalog. You can create multiple purchase orders from a request.
- Transfer Order - You can create a transfer order directly from a request to source hardware items and consumables from stockrooms.
- Consolidate PO - Select the optional Consolidate PO check box to combine the listed items with existing purchase orders.

Transfer Order and Purchase Order Created (Although should just be transfer orders)

Confirmation Prompt
8. Catalog Task Auto Closed. After you source the item, the catalog task is automatically closed.
9. Request Sourced. The Sourced checkbox is now automatically checked on the request. Purchase orders and Transfer Orders are shown via related lists on the request as needed as well.

Request Sourced
10a. Purchase Order Fulfillment. The purchase order process has multiple steps:
1. Open the Purchase Order

Purchase Order Form
2. Click Order
3. Click Receive when received. Received screen is shown

Receive Screen
4. Asset is received and set to the user who requested it
More information about the Receive process can be found here
10b. Transfer Order Fulfillment. The transfer order process has multiple steps:
1. Open the transfer order.

Transfer Order
2. Click "Ready for fulfillment" when ready. Stage moves to Requested
3. Click "Prepare for shipment" when ready. Stage moves to Shipment Preparation

Shipment Preparation
4. Click "Ship" when ready. Stage moves to fully shipped.
5. On the Transfer Order Line, Click Receive when received
6. On the Transfer Order Line, In order to get the "Deliver" button to appear, you need field service management installed, or you can adjust the UI Action condition or TransferOrderStageHandler script include to show the button.
11. Catalog Task Fulfillment. After the assets are now sourced and received, catalog tasks are generated for delivery.

Procurement Workflow: Item Sourced and Received
12. Close Catalog Tasks. Close Catalog Tasks as completed

Catalog Task for Configuration

Delivery Catalog Task
13. Requested Item Closed. When all the catalog tasks are completed, the requested item is closed
14. Request Closed. When all the requested items are closed, the request is closed
More information
Wiki on ServiceNow Procurement:
Demand Management
Contract Management
A contract is a binding agreement between two parties.
In the ServiceNow platform, contracts contain detailed information such as contract number, start and end dates, active status, terms and conditions statements, documents, renewal information, and financial terms.
Contract Management is enabled automatically in the base ServiceNow platform.
THE Contract Lifecycle
Contracts follow a lifecycle based on state and substate. This determines when they can be edited and when they are in compliance (expiration).
Contract States
State | Description
Draft | User adds information about the contract and specifies an approver.
Active | Contract was approved and has reached the specified start date.
Expired | Contract reached the specified end date. Expired contracts with an active renewal workflow that are waiting for approval have a substate of Awaiting Review. Expired contracts with an active renewal workflow where the renewal was approved, but the renewal date has not yet passed, have a substate of Renewal Approved. Expired contracts with no active renewal or extension pending workflow have an empty substate.
Canceled | Contract was discontinued and is no longer active.
Contract substates
Substate | Description
Awaiting Review | Contract is being prepared for review.
Under Review | Contract is sent to the approver and the approver is reviewing the contract.
Approved | Contract is reviewed and accepted by the approver.
Rejected | Contract is reviewed and declined by the approver.
Renewal Approved | Contract renewal is approved by the approver.
Renewal Rejected | Contract renewal is rejected by the approver.
Extension Approved | Contract extension is approved by the approver.
Extension Rejected | Contract extension is rejected by the approver.
None | No substate is specified.
Process
Create a contract
You need the contract_manager or admin role to create a contract.
1. In the Left Navigator Bar, go to Contract, and then under Insurance, Leases, Non-Disclosure, Maintenance, etc, click the type of contract you want to create.
Please note that some contracts like Software Licenses may function differently.
2. Click the New Button

Contract New Button
3. Fill in the fields and click submit. The full list of fields and what they do is listed here
4. If you filled in an approver, the contract now has a substate of "Under review"
5. The approver received an approval

Contract Management Approval
6. If the approver approves, the contract goes to state:active
There are also optional steps in the contract creation process:
- Add an asset to a contract
- Add a user to a contract
- Add a configuration item to a contract
- Add a document to a contract
Adjust a contract
You need the contract_manager or admin role to adjust a contract.
1. Open an existing contract
2. Click the Adjust button

Contract Adjust
3. Click Apply Changes to complete the adjustment
There are also optional steps in the contract adjust process:
3. Verify contract administrator assignment for notification
You need the contract_manager or admin role to adjust notifications.
This can be one of the most helpful (or most annoying) part of ServiceNow. It is important you adjust this.
When the contract.expiration event runs on the Contract [ast.contract] table each night, an email message is sent to the person identified as the contract administrator. This occurs at the following times.
- 90 days ahead of the contract expiration date
- 60 days ahead of the contract expiration date
- 30 days ahead of the contract expiration date
- On the contract expiration date
A user with the admin role can edit the contract.expiration condition check that processes contract notifications. Follow the procedure below to verify that the right contract administrator is assigned to the contract.
Procedure
- Navigate to Contract Management > Contract > All.
- Select a contract.
- Check that the Contract administrator field contains the correct name. A single name can be specified.
5. Terms and conditions
You can add terms and conditions to a contract to keep all documentation that is relevant to a contract in one location.

Contract Terms and Conditions
The terms and conditions can be searched and used in reports. If multiple terms and conditions records are added to a single contract, set an order for the records so they appear in a specific sequence. The terms and conditions fields become read-only after a contract is sent for approval.
Users with the contract_manager role can read contract history and add terms and conditions.
There are three procedures involved in adding terms and conditions to a contract, as follows.
- Create a terms and conditions record.
- Add the record to a contract.
- Build a terms and conditions document for the contract.
Create a contract rate card
A contract rate card provides detailed price information for a contract and enables you to generate expense lines for recurring expenses automatically. There can be multiple rate cards for the same contract.
You must activate Cost Management to use rate cards. You need the role of financial_mgmt_user, asset, or contract_manager use them as well.
In my opinion, this is only applicable unless you are doing a full cost management implementation. You can read about it here however.
Monitor a contract
You need the contract_manager or admin role to view contract history.
On any contract, you can view the Contract History Related list to see who edited the contract or view earlier versions.
You can also view 12 different contract reports in the base system as well. Those reports are just a start, you'll probably want to create your own reports as well.
More information
Here is an video tutorial on Contract Management
Release Management
Release Management encompasses the planning, design, build, configuration and testing of hardware and software releases to create a defined set of release components.
Plugins
Activate the Release Management plugin to use, which will also upgrade you to the newest version.
Table Structure
Table Name | Definition
Product [rm_product] | Represent whole products whose releases are being managed.
Release [rm_release] | Represent individual versions of the product.
Release Phase [rm_release_phase] | Represent the different stages of work required to complete a release.
Feature [rm_feature] | Represent each feature within the release.
Release Tasks [rm_task] | Represent tasks to create individual features.

Process
Define a product
A product might be an application, physical item, or service.
- Left Navigation Bar > Release > Products and click New.
- Fill out the form and click submit

Product
Planning Board
The Planning Board is an interface for manipulating the tasks related to releases for a particular product.
Use the release Planning Board
- Open the product record and select the Planning Board related link.
- On the list of releases associated with the product, click the name of the release to highlight it in green
Move a task from one release to another
- On the Planning Board, select the tasks to move
- Click the arrow for the target release

Planning Board
Define a release
- Navigate to the form of the appropriate parent Product.
- Scroll to the Releases related list and click New.

Releases under Product

Release
Because releases can have child releases, you can group minor releases under major releases.
Define a release phase
- From the Release form, use the Release Phases related list.
- Click New
- Fill out the form and click submit

Release Phase
Manage the release process
Once a product is defined, you can plan and execute a release.
- Create the release: Define the release record and child tasks.
- Scope the release: Define features for releases and child tasks.
While creating and scoping the release, use the Release Hierarchy related list on the Release Form to view the release as a hierarchy.

Release Hierarchy
Scope a release
You can scope a release from the Release form's Features related list.
- From the Release form, use the Features related list to define features for the release.
From the feature form, the Release Tasks related list can be used to define release tasks for the feature.

Feature

Release Task
Agile Development plugin
The Agile Development plugin further extends upon the Release Management v2 plugin by adding a lot more value to the application.
Task Table Relationship
Since releases are tied to the task table, you can easily tie them to changes, problems, etc. as well.
Shared Services
Shared services is the consolidation of business operations that are used by multiple parts of the same organization.
Shared services are cost-efficient because they centralize back-office operations that are used by multiple divisions of the same company and eliminate redundancy. Some companies use a chargeback system to bill divisions that use the service on a per-use, per-quarter or per-year basis. Other companies absorb the cost of shared services as part of the continuing cost of running the business. Today, most companies employ a shared services model for finance, human resources management (HRM) and information technology (IT).
Benefits OF SHARED SERVICES
- Economic - Higher productivity by consumer-like service portal and automated request fulfillment processes give employees more time for core business functions. Significantly reduce service delivery costs by driving standardization, consistency, and consolidation.
- Strategic - Achieve process and system standardization and meet increased demand with fewer full time employees.
- Quality - Improved information by using a common platform provides you with complete visibility into service usage, costs, errors, and bottlenecks. Develop service delivery best practices and establish centers of excellence.
- Speed - Automate and orchestrate interactions across departments to rapidly fulfill service requests.
POWER OF THE PLATFORM
Why is ServiceNow an ideal foundation for a shared services implementation? It is a single platform that can do so much and is designed with service management and consolidation in mind.
One Platform
Customer Service, IT, HR, and other departments can all use the same platform, sharing functionality and reusing customizations between departments. No integrations needed, you can easily connect different ServiceNow applications together within the platform.
One Knowledge Base
All your knowledge in one central location filtered for visibility with user criteria. No need to look in multiple sharepoint sites, sifting through word documents trying to find an answer. Have one central location for all your company and customer facing information.
One Service Portal
Your employees, partners, and customers gain easy access to all the consumer‑like business services you can now deliver through one portal. Provide your stakeholders with an easy way to submit, track, and be proactively alerted to the status of their requests for service.
One Code Base
Only primarily JavaScript code base to support. Most of that is declarative as well. You don't have be a coding wizard with a photographic memory to be good at ServiceNow. It is relatively easy compared to other systems.
Rapidly deliver cost‑effective and intuitive services to help your organization become a strategic business partner
Workflow and Ownership
Create services that streamline and automate interactions between departments. Task Assignments show who owns tasks and are not lost in emails and conversations.
Reporting and SLAs
Create a performance driven culture through measurement and feedback between departments. Manage service delivery through clear service level agreements and responsibilities.
Shared Services need a Platform
If you are going to merge processes, responsibilities, or departments you need a platform to manage it all. Using different applications deters people from that kind of initiative. I am biased of course, but I do truly believe ServiceNow is the best platform to start on that journey.
Cost Management
Cost management tracks configuration item costs. The costs can be allocated to business units and used in reports.
Features
- Use rate cards to properly track configuration item, contract, task, and labor costs
- Defining configuration item (CI) costs
- Tracking one-time costs for CIs
- Processing recurring CI costs to generate expense lines
- Distributing bulk costs to multiple expense line sources
- Tracking costs related to tasks and projects
- Aggregating configuration item costs and charging the total cost to a business service or application
- Allocating expense lines to business units with flexible allocation rules
- Tracking planned and actual budget costs by cost center
Activate
Turn on the plugin "Cost Management" in your ServiceNow instance. Not to be confused with Finance Service Management or Financial Management. Those are completely different applications. Kind of confusing I know!
Architecture
Before you start gathering requirements for Cost Management, it is important to read up on all the tables and code that runs it. There will likely be properties to adjust and slight business rule changes to make throughout the project.
Here you can read about the Cost Management Tables, properties, UI policies, business rules, and client scripts:
Rate Cards
There are four different types of rate cards in Cost Management.
CI Rate Card
A configuration item (CI) rate card is a group of recurring configuration item costs associated with multiple configuration items.
Setup of each of these rate cards involves:
- Creating a CI rate cards against CIs. You can pick the CIs with a filter or manually.
- Establishing a rate card cost for those CIs
For example, you'll likely setup CI rate cards for certain types of servers or network equipment.
You can tell how much an individual CI truly costs in terms of leases, purchases, and maintenance. ServiceNow uses Expense Lines, to add up all those costs. Also expense lines can be aggregated to apply all configuration item expenses to a parent business service or application with relationship paths.

CI Rate Card

Rate Card Cost
Contract Rate Card
Capture operating costs by generating expense lines representing the cost of a contract. Associate a contract to certain assets and costs of those assets are tied to the contract.
This is similar to a rate card cost, except the contract contains all the costs. Where as with a rate card cost the costs accumulate.

Contract Rate Card
Task Rate Cards
Task rate cards are templates used to define the type of task and the method of calculating the associated costs. They can help you determine the costs of a P1 incident or an emergency change for example.
There is two versions of Task Rate cards, a flat rate and "time worked" version of Task Rate Cards.
The Time Worked version uses the "Use Time Worked" checkbox. That way users can add up all the time spent on an incident and ServiceNow will automatically multiply it by their labor rate card to find out how much that incident or change really cost.

Task Rate Card (Flat Rate)

Task Rate Card (Using Time Worked)
Labor Rate Cards
Labor rate cards are templates used to define worker's labor rates when calculating task cost based on time worked. Uses a reference only rate code to align rates with an external system.
You will likely get labor rate cards from HR or Finance and will have to import them into the system. They are somewhat secret, but are only approximations of labor costs. Sometimes you match labor rate cards to a User's Title or Department, but usually Title.

Labor Rate Card
More information on how these rate cards work: Cost Sources
Using Distribution Costs and Rules
Distribution Costs are costs which can be divided among a group of records. For example, the cost of power at a datacenter which can be divided among the CIs in the datacenter. Distribution Rules determine how the Distribution Costs are divided among the CIs.

Distribution Cost Rule

Distribution Cost
Allocating Expenses
Expenses can also be allocated to a business entity that is responsible for the expense.
This is not considered charge-back or billing but could be used as a source for billing. The primary purpose of expense allocation is to represent the consumer of the process that has incurred some expense. This can be accomplished by defining expense allocation rules.
By using Expense Allocation Rules, you can distribute the costs to multiple departments, cost centers, or groups.
BUDGETS
Customers sometimes ask me "Can ServiceNow make Budgets?"
Yes, but not as typically expected. Budgets take all that you learned from Expense Allocations and drive up to a cost center. It is more an automatic process, the only numbers you can punch in are dates and your planned costs.
This is often an more accurate depiction of what the costs were. Although more difficult to float numbers around. :)
